Are you struggling to keep your aquarium water clean and your fish healthy? High nitrate levels can quietly harm your aquatic friends and cloud your tank’s beauty.
But don’t worry—reducing nitrate in your aquarium is easier than you think. You’ll discover simple, effective steps you can take right now to lower nitrate levels and create a vibrant, thriving underwater world. Keep reading to learn how to protect your fish and enjoy a crystal-clear aquarium every day.
Sources Of Nitrate In Aquariums
Nitrate builds up in aquariums naturally. It comes from many common sources.
Understanding where nitrate comes from helps keep water clean and fish healthy.
Fish Waste And Uneaten Food
Fish produce waste that breaks down into ammonia, then nitrite, and finally nitrate. Uneaten food also rots and adds to nitrate levels.
- Fish produce waste constantly
- Excess food decays quickly
- Both add to nitrate in water
- Regular cleaning reduces buildup
Decaying Plant Matter
Dead or dying plants release nitrogen compounds as they decay. This process raises nitrate levels in the tank.
| Plant Condition | Nitrate Impact |
| Healthy | Low |
| Dying | Moderate |
| Decaying | High |
Tap Water Contributions
Tap water often contains nitrate from its source. Adding water without testing raises nitrate levels.
To check tap water nitrate:
- Use a nitrate test kit
- Consider water treatment options
- Use reverse osmosis if needed

Credit: www.reddit.com
Effects Of High Nitrate Levels
Nitrate is a common chemical in aquariums. It forms when fish waste breaks down. High nitrate levels can harm your aquarium.
It is important to understand how nitrate affects your tank. This helps keep fish and plants healthy.
Impact On Fish Health
High nitrate can stress fish. Stress lowers their immune system. Fish become weak and sick more often.
Long exposure to nitrate causes slow growth. Some fish may lose color or stop eating. It can even cause death.
Algae Growth Issues
Nitrate is food for algae. When nitrate is high, algae grow fast. Too much algae makes the tank look dirty.
Algae can cover plants and decorations. This blocks light and harms plants. It also uses oxygen needed by fish.
Water Quality Deterioration
High nitrate means poor water quality. It can cause bad smells and cloudy water. This makes the tank unhealthy.
Dirty water can cause more fish diseases. It also harms beneficial bacteria that clean the tank.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Keeping nitrate levels low is important for a healthy aquarium. Regular maintenance helps remove waste and prevent nitrate buildup.
Simple actions like changing water and cleaning the tank reduce harmful nitrates. These steps keep fish safe and water clear.
Frequent Water Changes
Changing water regularly lowers nitrate concentration. It removes dissolved waste that fish produce over time.
Replace 10% to 20% of water weekly. Use dechlorinated water to avoid harming fish.
- Use a siphon or bucket for water removal
- Add new water slowly to avoid stress
- Check water temperature before adding
Gravel Vacuuming
Gravel traps leftover food and fish waste. Vacuuming gravel removes this debris and cuts nitrate buildup.
Use a gravel vacuum during water changes. Clean small sections each time to avoid disturbing fish.
- Move the vacuum slowly through the gravel
- Focus on areas with visible dirt
- Remove only 25% of gravel debris per cleaning
Filter Cleaning
Filters trap waste and help good bacteria grow. Cleaning filters removes debris but keeps beneficial bacteria safe.
Rinse filter media in tank water to protect bacteria. Avoid using tap water, which can kill helpful microbes.
- Clean filter parts every 2 to 4 weeks
- Replace filter media as directed by manufacturer
- Keep filter running during cleaning to maintain water flow

Credit: www.pond-planet.co.uk
Improving Filtration Systems
Reducing nitrate in your aquarium helps keep fish healthy. Filtration systems play a key role in lowering nitrate levels. Using the right filtration methods can make a big difference.
This guide covers ways to improve filtration by focusing on biological filters, nitrate-reducing media, and live plants.
Biological Filtration Enhancements
Biological filtration uses good bacteria to break down waste. These bacteria convert harmful ammonia into less harmful nitrate. Improving this process lowers nitrate buildup in the tank.
- Increase surface area in filters for more bacteria growth
- Use bio balls, ceramic rings, or sponge filters
- Keep water flow steady but gentle to help bacteria thrive
- Clean filter media carefully to avoid killing bacteria
Using Nitrate-reducing Media
Nitrate-reducing media help remove nitrate directly from the water. These materials support special bacteria that consume nitrate and turn it into harmless nitrogen gas.
| Media Type | How It Works | Ideal Use |
| Denitrifying Bio Media | Feeds bacteria that reduce nitrate | In canister or sump filters |
| Carbon-based Media | Adsorbs nitrate molecules | Short term nitrate removal |
| Zeolite | Removes ammonia, helps bacteria | Starter filter media |
Adding Live Plants
Live plants absorb nitrate as a nutrient. They reduce nitrate by using it to grow. Adding plants is a natural way to keep nitrate low in your aquarium.
- Choose fast-growing plants like hornwort or duckweed
- Place plants where they get enough light
- Trim plants regularly to keep them healthy
- Use root tabs if substrate lacks nutrients
Optimizing Feeding Habits
Feeding fish the right way keeps your aquarium healthy. Nitrate levels can rise if you feed too much or use poor-quality food.
By making a few changes, you can help keep nitrate levels low. This benefits both your fish and their environment.
Controlled Feeding Amounts
Feeding the right amount is key. Too much food can lead to waste and higher nitrate levels.
- Observe your fish while feeding to ensure they eat everything.
- Remove uneaten food after a few minutes to prevent decay.
- Feed small portions to make sure all food is consumed.
Choosing Quality Fish Food
Quality fish food can reduce waste and improve water quality. It is important to choose food that meets your fish’s dietary needs.
| Type of Fish | Recommended Food Type |
| Tropical Fish | High-protein pellets |
| Goldfish | Flakes with plant-based ingredients |
| Carnivorous Fish | Frozen or live food |
Using Chemical Treatments
High nitrate levels in aquariums can harm fish and plants. Chemical treatments help lower these levels quickly. They are easy to use and work well with other methods.
Using the right chemical treatment keeps your aquarium safe and clean. Always follow instructions carefully for best results.
Nitrate Removal Resins
Nitrate removal resins are special beads that soak up nitrates from water. They work by trapping nitrate ions, making the water safer for fish.
- Place resins in your filter or a separate media bag
- Replace resins as recommended by the manufacturer
- Monitor nitrate levels regularly to track progress
- Combine with regular water changes for best results
Water Conditioners
Water conditioners neutralize harmful chemicals and reduce nitrates. They are easy to add directly to the aquarium water.
| Type of Conditioner | Main Function | Use Frequency |
| Nitrate Neutralizer | Reduces nitrate toxicity | Weekly or as needed |
| Dechlorinator | Removes chlorine and chloramine | Every water change |
| Detoxifier | Neutralizes heavy metals and nitrates | After adding new water |
Employing Natural Nitrate Reducers
High nitrate levels can harm your aquarium’s health. Using natural nitrate reducers helps maintain balance. These methods are safe and effective for your fish and plants.
Natural nitrate reducers offer a sustainable way to keep your aquarium clean. They work by removing excess nitrates from the water. This ensures a healthier environment for your aquatic life.
Nitrate-consuming Plants
Plants play a big role in reducing nitrates. They absorb nitrates through their roots as they grow. This natural process helps clean the water.
Some plants are especially good at consuming nitrates. These include hornwort, anacharis, and duckweed. Adding these plants can improve your aquarium’s water quality.
- Hornwort grows fast and uses up nitrates quickly.
- Anacharis can thrive in different water conditions.
- Duckweed covers the water surface, absorbing nitrates.
Beneficial Bacteria Additives
Bacteria are essential for breaking down waste in aquariums. Certain bacteria can convert nitrates into harmless nitrogen gas. This process is called denitrification.
Adding beneficial bacteria additives boosts this process. These products introduce helpful bacteria into your aquarium. They work hard to keep nitrate levels low.
- Choose bacteria additives designed for nitrate reduction.
- Follow the product instructions for best results.
- Regular use can help maintain water balance.
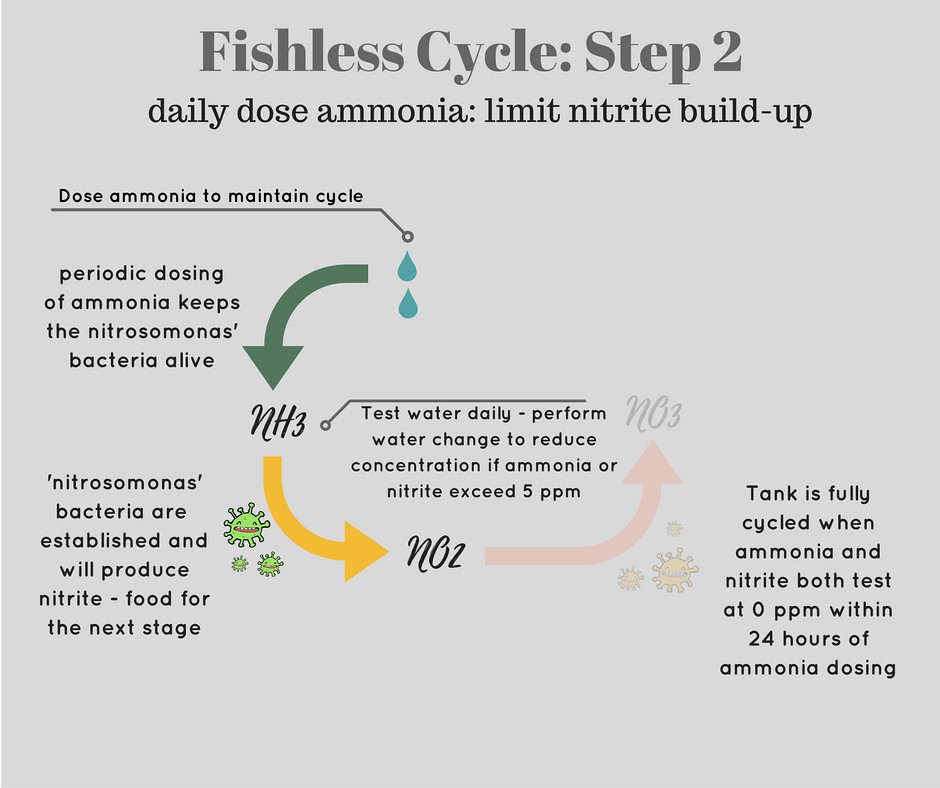
Credit: spec-tanks.com
Monitoring Nitrate Levels
Keeping nitrate levels low is important for a healthy aquarium. High nitrate can harm fish and plants.
Regular monitoring helps you catch problems early. It lets you take action before nitrate gets too high.
Testing Kits And Frequency
Use a reliable nitrate test kit to measure levels in your tank water. These kits are easy to use and give quick results.
Test nitrate at least once a week. More frequent testing helps if you have many fish or plants.
- Choose kits with clear instructions
- Test weekly for regular tanks
- Test more often in busy or new tanks
- Keep a log of your test results
Interpreting Test Results
Low nitrate levels are best for fish health. Aim for less than 20 ppm (parts per million).
If nitrate is between 20 and 40 ppm, watch it carefully. Above 40 ppm can stress fish and cause algae growth.
| Nitrate Level (ppm) | Meaning | Action Needed |
|---|---|---|
| 0-20 | Safe and healthy | Maintain current care |
| 21-40 | Moderate level | Check water and consider changes |
| 41+ | High and risky | Do water changes and reduce feeding |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes High Nitrate Levels In Aquariums?
High nitrate levels mainly result from fish waste, uneaten food, and decaying plants. Overfeeding and poor filtration worsen nitrate buildup. Regular tank maintenance helps control these sources effectively.
How Often Should I Change Water To Reduce Nitrate?
Perform partial water changes of 20-30% weekly. This helps dilute nitrates and maintain a healthy aquarium environment. Consistent changes prevent nitrate accumulation and promote fish well-being.
Can Live Plants Help Lower Aquarium Nitrate?
Yes, live plants absorb nitrates as nutrients, reducing their concentration. Fast-growing plants like hornwort and water sprite are especially effective in nitrate control.
Does Aquarium Filtration Remove Nitrates Effectively?
Standard filters mainly remove debris, not nitrates. Specialized filters like denitrifying or biological media can help reduce nitrates by promoting beneficial bacteria growth.
Conclusion
Reducing nitrate in your aquarium keeps fish healthy and water clear. Regular water changes help remove nitrate build-up. Using live plants absorbs nitrates naturally. Avoid overfeeding to limit waste and nitrate rise. Proper filtration supports a balanced tank environment. Test water often to track nitrate levels.
Small, simple steps make a big difference. Your fish will thrive in cleaner water. Keep your aquarium safe and beautiful with these tips.