Have you ever wondered why your betta fish sometimes flares its fins or chases its reflection? Understanding betta social behavior can transform how you care for your fish and improve its happiness.
When you know what your betta is trying to tell you, you can create a peaceful environment where it thrives. You’ll discover the secrets behind your betta’s actions and learn simple tips to keep your aquatic friend calm and content.
Keep reading, because unlocking these behaviors could change your entire experience with bettas.

Credit: aquabettas.com
Betta Communication
Betta fish use many ways to talk without sounds. They show feelings and intentions with their bodies.
Understanding their signals helps you know what your betta needs or feels.
Body Language Signals
Betta fish move their bodies to send messages. They change posture to show moods like fear or anger.
A betta may swim fast or freeze to warn others or protect itself.
- Flared gills mean the betta feels threatened or wants to show strength.
- Slow swimming shows calmness or rest.
- Rapid darting can mean excitement or stress.
- Hiding signals fear or shyness.
Color Changes
Betta colors change to express feelings. Bright colors often show health or readiness to mate.
Darker or dull colors can mean stress, illness, or submission.
- Bright colors attract mates and warn rivals.
- Dull colors help bettas hide from danger.
- Color shifts can happen quickly during fights or displays.
Fin Displays
Bettas use their fins to communicate. They spread fins wide to look bigger and more powerful.
Clamped fins often show fear or discomfort. Fin movements also help show mood and intent.
- Flared fins mean aggression or courtship.
- Clamped fins mean fear or illness.
- Quivering fins can mean excitement or nervousness.
Territorial Nature
Betta fish are known for their strong territorial behavior. They often guard their space to feel safe. This behavior is natural and important for their well-being.
Understanding how bettas act in their territory helps keep them healthy and happy. It also prevents fights and stress in the tank.
Establishing Boundaries
Bettas set clear boundaries in their tank to mark their space. They use visual signals like flaring fins and colors. These signs warn other fish to stay away.
Decorations and plants help create natural borders. Bettas feel more secure when they have their own area. This reduces stress and aggression.
- Use plants or decorations to divide the tank
- Give each betta enough space to swim freely
- Watch for signs of boundary crossing
Aggression Triggers
Bettas become aggressive when they feel their territory is threatened. Seeing another betta nearby can cause them to flare and attack. Sudden movements or reflections can also trigger aggression.
Overcrowding the tank or placing mirrors close can increase fights. Stress and lack of hiding spots make bettas more aggressive too.
- Presence of other male bettas nearby
- Reflections on the tank walls
- Sudden movements or changes in the environment
- Small tank size with limited hiding spots
Conflict Resolution
Bettas resolve conflicts by showing dominance or retreating. Often, one fish will back down after a short fight. Providing enough space helps reduce these conflicts.
Using tank dividers or separate tanks can keep bettas safe. Adding plants and hiding spots lets fish escape if they feel threatened.
- Use clear dividers to separate aggressive bettas
- Add plants or decorations for hiding
- Keep one betta per tank if possible
- Watch fish behavior to prevent fights early
Social Hierarchy
Betta fish show clear social hierarchy in their groups. This hierarchy affects how they act around each other.
Understanding this social order helps keep bettas healthy and reduces fights in tanks.
Dominant Vs Submissive Roles
In a betta group, some fish become dominant while others stay submissive. Dominant bettas control the space and food.
Submissive bettas avoid fights and stay in less crowded areas. They often show less bright colors and less aggressive behavior.
- Dominant bettas flare fins and chase others.
- Submissive bettas hide or swim away quickly.
- Dominance affects access to food and resting spots.
Group Dynamics
Betta fish form groups with clear roles to avoid constant fighting. Each fish learns its place in the group.
Groups with balanced roles have less stress and more peaceful interactions. This balance helps bettas live longer.
- Dominant fish lead the group.
- Submissive fish follow and avoid conflict.
- Group size affects how roles are formed.
Influence On Behavior
Social hierarchy shapes how bettas act daily. Dominant bettas are more active and aggressive.
Submissive bettas show shy and calm behavior. Their social rank influences their feeding and movement.
- Dominant bettas show brighter colors to show strength.
- Submissive bettas stay hidden to avoid fights.
- Hierarchy affects how bettas interact with tank mates.
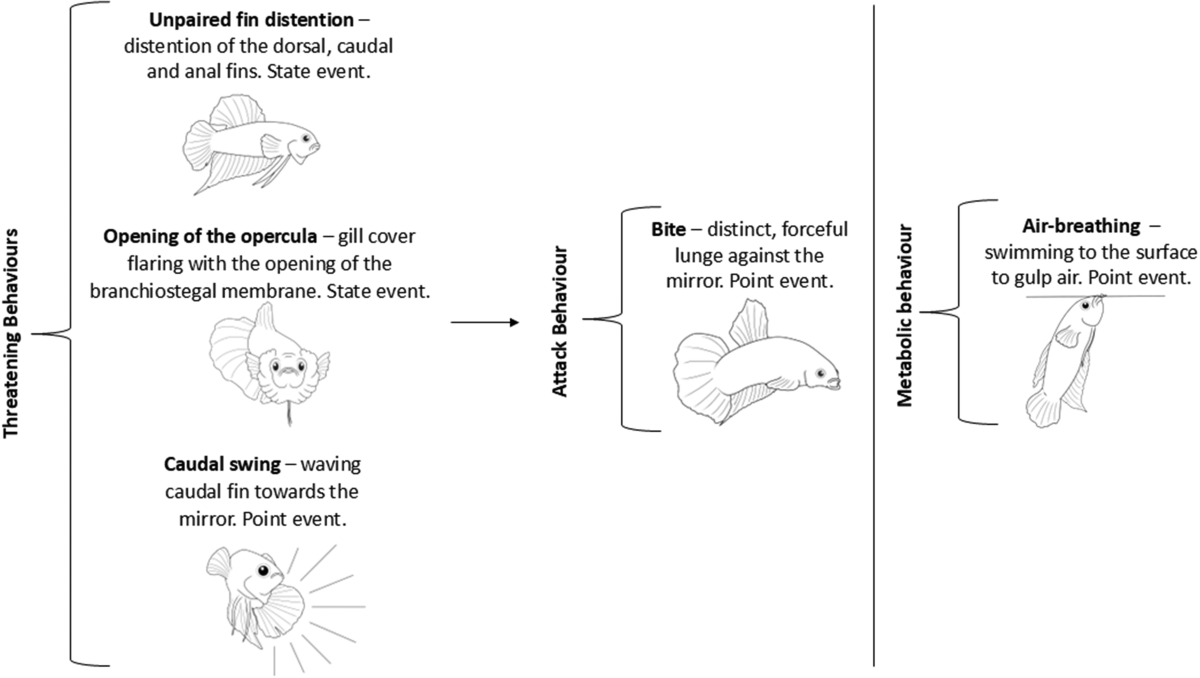
Credit: link.springer.com
Breeding Interactions
Betta fish show unique behaviors during breeding. These actions help them find mates and raise young. Understanding these behaviors is important for betta care.
Breeding interactions include courtship rituals, nest building, and parental care. Each stage has special behaviors that ensure successful reproduction.
Courtship Rituals
Male bettas display bright colors to attract females. They flare their fins and spread their bodies wide. This shows strength and health.
The male swims in circles around the female. He may also shake his body to get her attention. These actions encourage the female to respond.
- Bright color display
- Flaring fins and gills
- Swimming in circles
- Body shaking
Nest Building
Male bettas build bubble nests at the water surface. They blow bubbles that stick together to form a floating cluster. This nest holds the eggs after spawning.
The male keeps the nest intact by adding more bubbles. He also guards the area to protect it from threats. The nest is a safe place for the eggs.
- Blowing bubbles to form nest
- Adding bubbles to maintain nest
- Choosing calm water surface
- Guarding the nest area
Parental Care
After spawning, the male gathers the eggs and places them in the bubble nest. He keeps the eggs safe by staying near the nest. The male watches over the eggs until they hatch.
The male gently picks up fallen eggs and returns them to the nest. He also chases away other fish to protect the young. Parental care ends when the fry start swimming freely.
- Collecting eggs in bubble nest
- Protecting nest from intruders
- Returning fallen eggs to nest
- Guarding fry until free swimming
Living With Other Fish
Betta fish are often kept alone in small bowls, but they can thrive in a community tank with compatible tankmates. In fact, living with other fish can be beneficial for your betta’s social and physical health.
Compatible Tankmates
When choosing tankmates for your betta, look for peaceful and calm fish that won’t harass or fin-nip your betta. Some good options include:
- Neon Tetras: These small, schooling fish are easy to care for and add movement to the tank.
- Corydoras Catfish: These small catfish are good for cleaning up food debris and are generally peaceful.
- Harlequin Rasboras: These active fish are easy to care for and add color to the tank.
Avoiding Stress
Stress can be a major problem for betta fish, especially when they’re living with other fish. To avoid stress, make sure to provide plenty of hiding places and plants for your betta to retreat to when feeling overwhelmed.
Avoid overcrowding the tank, and make sure to provide plenty of space for your betta to swim and explore. Also, avoid placing your betta near strong water currents or loud noises.
Safe Community Setups
Creating a safe and harmonious community tank requires some planning and research. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Research the specific needs and personalities of each fish species before adding them to the tank.
- Start with a small group of fish and gradually add more as the tank becomes more established.
- Provide plenty of hiding places, plants, and visual barriers to help reduce stress and aggression.
- Monitor the tank closely and be prepared to make adjustments as needed.
Environmental Impact On Behavior
Betta fish show different behaviors based on their surroundings. Their environment shapes how they act daily.
Understanding these effects helps owners create a better home for bettas. This keeps them healthy and happy.
Tank Size And Layout
Tank size affects how bettas behave. Small tanks can stress them and cause aggression.
A larger tank gives bettas space to swim and explore. The layout with hiding spots helps reduce stress.
- Minimum 5 gallons for one betta
- Include plants and decorations for hiding
- Open swimming areas improve activity
Water Conditions
Water quality changes bettas’ mood and health. Clean water keeps them calm and active.
Temperature, pH, and hardness affect behavior. Bettas prefer warm, stable water to feel safe.
- Keep temperature between 76°F and 82°F
- Maintain pH around 6.5 to 7.5
- Change water regularly to avoid toxins
Enrichment And Stimulation
Bettas need mental and physical stimulation to stay healthy. Bored fish may become lazy or stressed.
Adding toys, plants, and mirrors can boost their activity. Changing the tank setup keeps bettas curious.
- Use live or silk plants for natural hiding
- Place floating toys for interaction
- Limit mirror time to avoid stress

Credit: tropicflow.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Betta Fish Social Behavior?
Betta fish are territorial and often aggressive toward others. Males especially defend their space. However, they can show curiosity and interaction in non-threatening environments.
Can Betta Fish Live With Other Fish?
Betta fish can live with certain peaceful species. Avoid fin-nippers or other aggressive fish. Proper tank size and hiding spots help reduce conflicts.
How Do Betta Fish Communicate?
Betta fish use body language like flaring fins and changing colors. These behaviors signal dominance, stress, or readiness to mate. Understanding these cues helps in care.
Why Do Betta Fish Flare Their Fins?
Flaring is a display of aggression or courtship. It helps establish dominance or attract mates. Excessive flaring may stress the fish, so monitor their behavior carefully.
Conclusion
Betta fish show many social behaviors that tell us about their needs. They can be aggressive or calm depending on their environment. Understanding these behaviors helps keep them healthy and happy. Each Betta is unique, so watch closely to learn what they like.
Give them space and a good tank to thrive. Enjoy the beauty and personality of your Betta every day. Caring for them means respecting their social nature and habits. Simple steps make a big difference in their life.