Are you struggling to keep your juvenile fish healthy and growing strong? Feeding young fish the right way can make all the difference in their survival and development.
If you want to see your fish thrive, you need to know the best feeding methods that suit their delicate needs. You’ll discover simple, effective tips that can transform how you care for your juvenile fish. Keep reading to unlock the secrets to healthy, happy fish that will brighten your aquarium.

Credit: www.reluctantgourmet.com
Selecting Proper Food
Choosing the right food for juvenile fish is very important. Proper food helps young fish grow healthy and strong. It also supports their immune system and activity level.
This guide explains different types of juvenile fish food, their nutritional needs, and the choice between homemade and commercial options.
Types Of Juvenile Fish Food
Juvenile fish require food that is easy to eat and digest. Their food varies by type and size. Many foods are made to meet these needs.
- Live food, like baby brine shrimp and daphnia
- Frozen food, such as bloodworms and tubifex worms
- Pellets and flakes made for young fish
- Gel food that softens in water for easy eating
Nutritional Requirements
Young fish need the right balance of nutrients. Protein is key for growth. Fat provides energy. Vitamins and minerals keep fish healthy.
| Nutrient | Purpose | Common Sources |
| Protein | Builds muscles and tissues | Live food, pellets, flakes |
| Fat | Energy and cell function | Fish oils, frozen food |
| Vitamins | Supports immune system | Vegetable matter, enriched flakes |
| Minerals | Bone and scale health | Balanced commercial food |
Homemade Vs Commercial Options
Both homemade and commercial foods have pros and cons. Homemade food lets you control ingredients. Commercial food offers balanced nutrients.
- Homemade food can include boiled vegetables, mashed peas, or live baby brine shrimp.
- Commercial food is easy to store and feeds many fish at once.
- Homemade food may spoil quickly and needs careful preparation.
- Commercial food is tested for nutrition but may contain fillers.
Feeding Frequency
Feeding juvenile fish often helps them grow strong and healthy. Young fish need regular meals to get the energy and nutrients they require.
It is important to set a feeding routine and watch your fish closely. This helps prevent feeding problems and keeps your fish active.
Daily Feeding Schedule
Juvenile fish should be fed several times a day. Small, frequent meals are better than one large meal. This keeps their digestion steady and reduces waste.
- Feed 3 to 4 times daily
- Offer small amounts each time
- Observe fish eating to avoid leftover food
- Feed at consistent times every day
Adjusting Based On Growth
As juvenile fish grow, their feeding needs change. Increase the food amount slowly to match their size. Adjust feeding frequency if fish seem hungry or full.
| Growth Stage | Feeding Frequency | Amount per Feeding |
| Newly hatched | 4 times a day | Very small portions |
| Small juveniles | 3 times a day | Small portions |
| Larger juveniles | 2 to 3 times a day | Medium portions |
Signs Of Overfeeding
Too much food can harm juvenile fish. Watch for signs that show overfeeding. Act quickly to protect your fish’s health.
- Cloudy water or strong odor
- Uneaten food on tank bottom
- Fish swimming slowly or showing bloating
- Increased algae growth in the tank
Feeding Techniques
Feeding juvenile fish properly is important for their growth and health. Using the right feeding techniques helps young fish get the nutrients they need.
Different methods work best depending on the species and environment. This guide covers common ways to feed juvenile fish effectively.
Hand Feeding Tips
Hand feeding lets you watch your fish closely and check their health. It builds trust between you and the fish.
Offer small amounts of food at a time. Feed gently to avoid stressing the fish. Use tweezers or fingers carefully.
- Feed in calm waters to reduce stress
- Use small pieces of food for easy eating
- Feed multiple times a day in small portions
- Watch how fish respond to adjust feeding
Using Feeding Tools
Feeding tools help deliver food precisely and keep the tank clean. They can reach areas where fish like to eat.
Tools like pipettes, feeding rings, or automatic feeders make feeding easier. They reduce waste and avoid overfeeding.
- Pipettes drop food gently near fish
- Feeding rings keep food in one place
- Automatic feeders provide steady feeding times
- Use soft brushes to clean leftover food
Encouraging Natural Foraging
Natural foraging helps juvenile fish develop hunting skills. It mimics their behavior in the wild and keeps them active.
Place food in different spots or use live food. This encourages fish to search and work for their meals.
- Scatter small food pieces around the tank
- Use live or frozen foods like brine shrimp
- Add plants or hiding spots for exploration
- Feed at varying times to mimic natural conditions
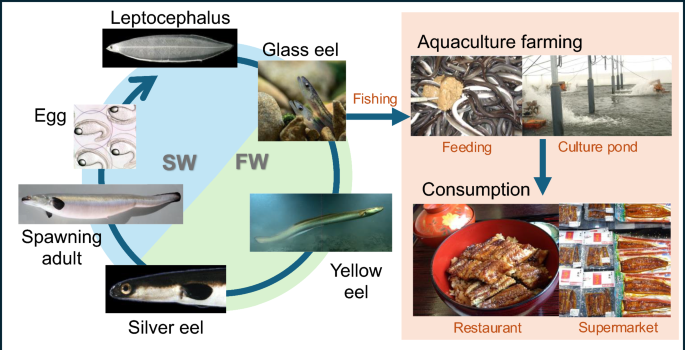
Credit: www.nature.com
Water Quality And Feeding
Feeding juvenile fish needs care to keep water clean. Good water quality helps young fish grow healthy.
Too much food can pollute the water and harm the fish. It is important to balance feeding with tank care.
Impact Of Feeding On Water
Overfeeding creates leftover food and waste. This raises ammonia and toxins in the water. Poor water quality can cause diseases.
Feed small amounts several times a day. Remove uneaten food quickly to avoid water pollution.
Maintaining Clean Environment
- Change 10–20% of the water weekly
- Use a good filter to remove waste
- Clean the tank walls and substrate regularly
- Test water parameters often to check quality
Keeping the tank clean helps fish stay healthy and active. A clean environment reduces stress and disease.
Balancing Feeding And Filtration
| Feeding Tips | Filtration Tips |
| Feed small amounts 3 times daily | Choose filter suitable for tank size |
| Remove uneaten food within 5 minutes | Clean or replace filter media monthly |
| Use high-quality, digestible food | Use biological filtration for ammonia control |
Good feeding and filtration work together. They keep water clean and fish healthy.
Common Feeding Challenges
Feeding juvenile fish can be tricky for many aquarists. Young fish have special needs and behaviors.
Understanding common feeding challenges helps keep fish healthy and growing well.
Dealing With Picky Eaters
Some juvenile fish refuse certain foods or eat too little. This can slow their growth.
- Offer a variety of food types like flakes, pellets, and live food.
- Feed small amounts often to avoid waste.
- Try changing the food texture or size to find what they prefer.
- Observe their behavior to learn their favorite food.
Preventing Food Waste
Uneaten food pollutes the water and can harm juvenile fish. It is important to feed the right amount.
| Feeding Tip | Reason |
| Feed small portions | Fish eat all food quickly, reducing leftovers |
| Remove uneaten food after 5 minutes | Prevents water contamination |
| Use sinking food for bottom feeders | Food reaches all fish types, avoiding waste |
| Feed during active times | Fish are more likely to eat all food |
Handling Aggressive Behavior
Some juvenile fish show aggression during feeding. This can stress weaker fish and block food access.
Try these methods to reduce aggression:
- Feed in multiple spots to spread fish out.
- Use feeding rings or containers to limit food area.
- Separate very aggressive fish if needed.
- Feed smaller amounts more often to reduce competition.
Monitoring Growth And Health
Juvenile fish need proper care to grow healthy. Monitoring their growth and health is essential for their development.
This guide will explore the best feeding methods and how to track growth rates, identify nutritional deficiencies, and adjust diets for optimal health.
Tracking Growth Rates
Tracking growth rates helps you understand the development of juvenile fish. It is important to measure their size regularly.
| Age (weeks) | Average Length (cm) |
| 1 | 1.2 |
| 2 | 1.8 |
| 3 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 3.0 |
Identifying Nutritional Deficiencies
Recognizing nutritional deficiencies is crucial for the health of fish. Look for signs such as slow growth or color changes.
- Pale gills can indicate a lack of iron.
- Faded colors may suggest low vitamin levels.
- Reduced appetite could mean protein deficiency.
Adjusting Diet For Optimal Health
Adjusting the diet of juvenile fish ensures they receive proper nutrition. Consider varying their food to provide a balanced diet.
Feed them a mix of pellets and live food for a diverse diet.

Credit: www.wired2fish.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Food For Juvenile Fish?
Juvenile fish thrive on high-protein, small-sized foods like baby brine shrimp and finely crushed flakes. These support healthy growth and development.
How Often Should Juvenile Fish Be Fed Daily?
Feed juvenile fish 3 to 5 times daily in small amounts. Frequent feeding helps meet their high energy and growth needs.
Can Live Food Improve Juvenile Fish Health?
Yes, live foods like daphnia and microworms enhance nutrition and stimulate natural hunting behavior in juvenile fish, boosting health and vitality.
Should Juvenile Fish Be Fed Differently Than Adults?
Yes, juveniles need smaller, more frequent meals with higher protein content to support rapid growth compared to adult fish diets.
Conclusion
Feeding juvenile fish well helps them grow strong and healthy. Use small, frequent meals to match their tiny mouths. Choose nutritious food that suits their species and stage. Watch their behavior to avoid overfeeding or waste. Clean water keeps fish safe and happy.
Good feeding habits lead to lively, thriving fish tanks. Keep learning and adjust methods as fish grow. Simple care makes a big difference in their life. Your effort shows in their bright colors and energy. Healthy fish bring joy to any aquarium.